
What Is Security?
Overview
Environments involving electronic devices are exposed to various threats including unauthorized access, information leaks and data falsification.
Similarly, this system handles data for which there is a risk of security-related issues.
To avoid such risk, it is important to put in place safety measures from the perspective of information security.
- Before connecting to a network, it is recommended to first consider putting in place the security measures detailed in this chapter.
Security
The aim of security is to maintain information confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
The system is equipped with various functions for ensuring these three requirements.
This section describes these 3 requirements with along with examples of countermeasures.
For details about the countermeasures, refer to the following.
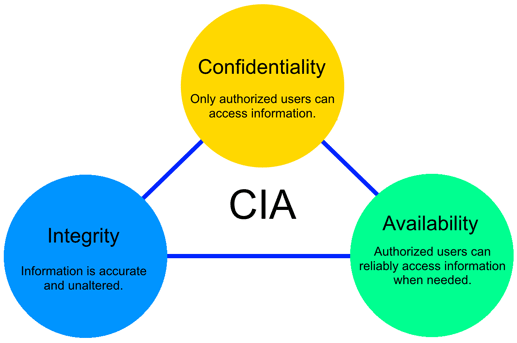
Confidentiality
Aims to ensure that only permitted users may access information. Using encryption and setting restrictions on accessing data also helps to improve confidentiality.
Example of Countermeasures:
Encrypting communications (Encrypting Communications)
Secure printing (Secure Printing)
Authentication (Overview of User Authentication)
etc.
Integrity
Aims to ensure a state in which information is not tampered with, and that information remains accurate and complete.
Example of Countermeasures:
Digital Signatures ([S/MIME Communication Settings])
Firmware Diagnosis ([Self-Diagnostic Setting])
etc.
Availability
Aims to ensure a state in which the necessary people can access the necessary information when needed.
For example, losing access to your data due to a system failure means that availability cannot be maintained.
Example of Countermeasures:
Backing up (Backing Up Data)
etc.

 in the upper-right of a page, it turns into
in the upper-right of a page, it turns into  and is registered as a bookmark.
and is registered as a bookmark.