Image Quality: Registering the Output Profile (Printer Profile)
Measure the hue that can be reproduced by the machine for a certain paper type, and calculate the CMYK values to be used to produce the desired color. Use that result to create a "printer profile" as definition.
To prevent color reproducibility from varying by paper type, it is recommended that you prepare a printer profile for each paper type (colored paper, coated paper, etc.) and use them separately.
• Meaning and Purpose of Output Profiles
The result (hue, shade, tinge) may be different for different paper types even when the same printing conditions are applied. This is due to the differences in toner fusing, paper whiteness, light reflectance, and other properties among paper types.
Using the appropriate output profile, you can minimize the variation and influence of such properties specific to a paper type and print in colors close to the standard.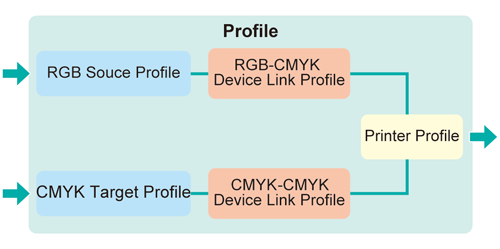
The following five types of profiles can be managed via Color Centro:
RGB source profile, CMYK target profile, Printer profile, RGB-CMYK device link profile, and CMYK-CMYK device link profile.For details about frequently output job settings, refer to Image Quality: Registering the Color Configuration.
There are profiles that are provided by the manufacturer and those that can be downloaded from the Internet.
Profiles other than RGB source profiles can be created.
•When to perform
When certain paper types are used frequently
When you wish to produce colors more accurately than the printer profile in use
When neither the calibrations nor Pre-output Image Quality Adjustment improves the hue
•Intended Environment
Operating system | Windows 7 |
Application | Color Centro 2.0 |
Printer driver | PS Plug-in Driver |
Image Controller | Image Controller IC-602 |
Instrument | i1Pro |
Paper type/thickness | Coated GL 128 g/m2 / 33 lb Bond (A3 / Loaded in Tray 1) |
* The sample screen may be different from the actual display depending on your system environment and application version/revision.
•Workflow
• Related Section
•Precautions
To reproduce stable colors, in addition to regular calibration, make other pre-output image quality adjustments as necessary, such as when changing screens or papers or when hue is important. For details, refer to Pre-output Image Quality Adjustment.