User's Guide
Constructing a Single Sign-on Environment for the SMB Transmission
By using the user authentication information (login name and password) of this machine as SMB destination authentication information (host name and password), you can avoid the problem of having to specify SMB destination authentication information, allowing construction of a single sign-on environment for SMB transmission.
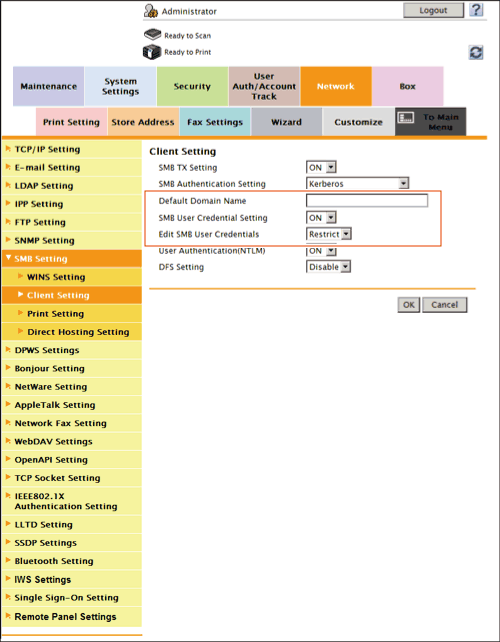
In the administrator mode, select [Network] - [SMB Setting] - [Client Setting], then configure the following settings.
| Settings | Description |
|---|---|
[Default Domain Name] | Enter the default domain name to be added to the host name of the destination at SMB transmission (using up to 64 characters). The default domain name cannot be prefixed by an asterisk (*). If the domain name of the destination is not specified by the user when sending data using SMB, the domain name specified here is added. This item is not required when Active Directory is used as an authentication server. |
[SMB User Credential Setting] | When using the user authentication information (login name and password) of this machine as SMB destination authentication information (host name and password), select [ON]. If Active Directory is used as an authentication server, the domain name of Active Directory is added to the login name. When other authentication method is used, the domain name entered at [Default Domain Name] is added. [OFF] is specified by default. |
[Edit SMB User Credentials] | If you have selected [ON] at [SMB User Credential Setting], select whether to allow registration of the SMB destination including authentication information same as that for user authentication. When you want to allow only users whose authentication information for user authentication matches that for SMB destination to access the SMB destination, select [Restrict]. [Restrict] is specified by default. |