Automatically Sorting Incoming Faxes (TSI Routing)
TSI Routing
TSI (Transmitting Subscriber Identification) Routing is a function that automatically sorts incoming faxes into preset boxes or redirects them to shared folders in computers or E-mail addresses based on the fax numbers of the senders. There is no need to sort printed faxes for each recipient and no risk of missing a fax. To use the TSI Routing function, it is required to preset boxes to which faxes are to be sorted and forwarding destinations. Routing destinations can be registered for up to 256 fax numbers (TSIs).
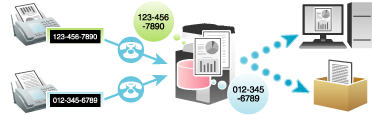
If the routing destination is not a fax destination, the fax is converted into the file format specified as the default in the fax/scan mode.
If the optional Extension Memory and i-Option LK-110 v2 are installed on this machine, received faxes can be converted into specified file types for forwarding destinations before they are forwarded. The file types able to be specified are PDF, XPS, and TIFF. Some models provide Extension Memory as standard. For details, refer to Here.
By default, a received fax is printed without being forwarded if it was not successfully distributed.
This function cannot be used together with the following functions.
Memory RX, Forward TX, PC-Fax RX
Operations required to use this function (for the administrator)
Enabling the TSI Routing function. Also, register fax numbers (TSIs) of senders targeted for forwarding, forwarding destinations, and file type. You can specify the following forwarding destinations.
Fax
E-Mail
SMB
FTP
WebDAV
User Box
Internet Fax
IP Address Fax
Group
For details on how to configure the settings, refer to Here.